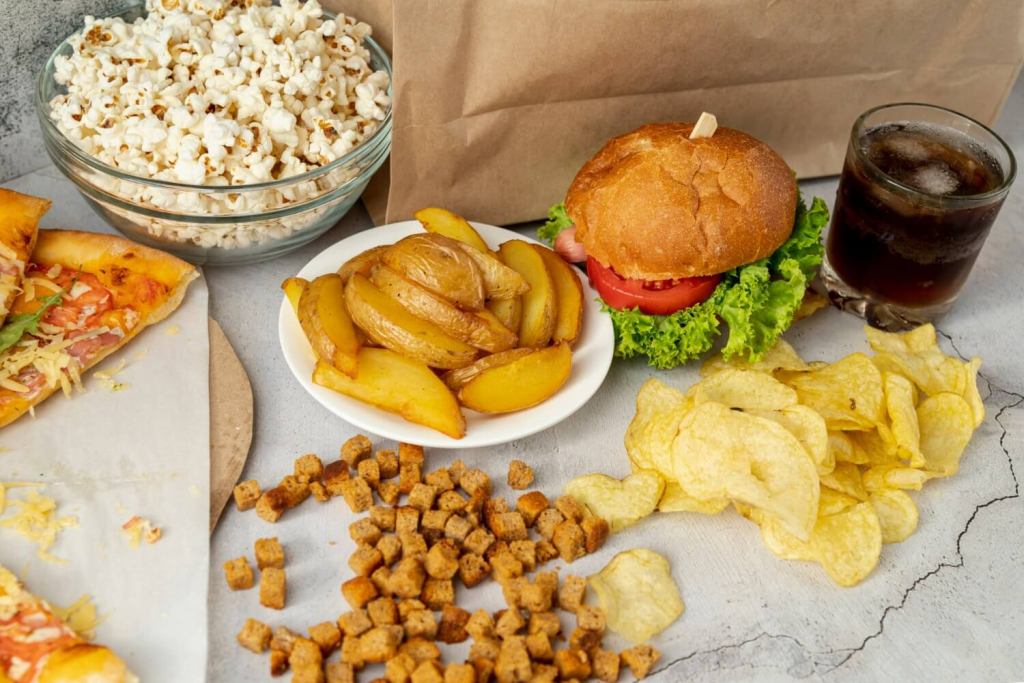
Most foods we consume have gone through some level of food processing before they make it to our plates.
In the Philippines, the current health status of the population reflects a mix of progress and concern. While access to foods fortified with beneficial vitamins and minerals has improved, the effects of processed foods on health are increasingly in the spotlight.
According to the World Health Organization, non-communicable diseases like cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and certain cancers are on the rise, many of which are linked to excess calorie intake, poor diet quality, and a shift toward ultra-processed diets.
Understanding the foods in your pantry is key to making better choices for human health. Read on to explore what processed foods are, common examples in Filipino kitchens, the health implications of ultra-processed food consumption, and practical tips for a healthy diet.

What are Processed Foods?
Processed food simply refers to any food that has been altered from its natural state through methods like cooking, freezing, canning, or adding processed culinary ingredients such as salt, sugar, or oil.
The NOVA Food Classification System
The NOVA food classification system developed by researchers groups foods into categories ranging from unprocessed foods (like fresh fruits and vegetables) to ultra-processed foods (such as sugary drinks and packaged snacks).
While some processing makes foods safer by eliminating harmful bacteria (like pasteurizing milk) or enhances nutritional value (like fortifying breakfast cereals), other processing methods add artificial flavors, artificial sweeteners, and high fructose corn syrup, which can lower the overall nutritional quality of the food consumed.
Common Processed Foods in the Philippines
Filipino kitchens are full of both minimally processed foods and heavily processed items.
Some of the most popular processed food you can find in your kitchen include:
- Processed meats like tocino, longganisa, and hot dogs
- Fried chicken and other fast-food staples
- Frozen meals for quick food preparation
- Breakfast cereals fortified with vitamins
- Canned goods like sardines, corned beef, and luncheon meat
- Packaged snacks with artificial flavors
- Sugary drinks with high fructose corn syrup

7 Things About Processed Foods You Need to Know
With a lot of ultra-processed foods in your pantry, you have to be equipped with the correct information about these foods.
Here are key facts about processed food you need to know:
1. Not All Processing is Bad
A key takeaway from research, including systematic reviews and meta-analyses, is that some processing actually improves nutritional value.
Some food processing, like milling whole grains into brown rice, removes inedible husks, making them more accessible. The Food and Agriculture Organization even promotes certain processing techniques to reduce harmful bacteria and improve public health.
2. Ultra-Processed Foods Have Strong Links to Chronic Diseases
Studies like the Nurses’ Health Study and prospective cohort studies have shown a statistically significant link between the consumption of ultra-processed and chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus, breast cancer, and cardiovascular disease.
This is partly because ultra-processed foods often contain more saturated fat, refined carbs, and food additives, which lead to excess calorie intake and excess weight over time.
3. Portion Sizes Influence Body Weight
In many cases, ad libitum food intake (eating freely without restriction) of ultra-processed foods leads to higher body mass index and body weight gain.
Experimental evidence from inpatient randomized controlled trials has demonstrated that when participants with a high consumption of ultra-processed food, they unintentionally consume more calories compared to when eating minimally processed or unprocessed foods.
4. Some Additives Can Impact Human Health
While many food additives in processed food are considered safe, studies suggest that certain artificial sweeteners, colorants, and advanced glycation end products formed during frying can contribute to adverse health outcomes, including metabolic syndrome.

5. Minimally Processed Foods are Key to a Healthy Diet
Nutrition experts emphasize balancing your diet with minimally processed foods such as fresh fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains like brown rice.
These foods provide beneficial nutrients, essential amino acids, and often have fewer calories compared to frozen meals or fast food.
6. Food Preparation Habits Matter
Even if you choose minimally processed ingredients, deep frying or adding excessive oil, salt, or sugar during food preparation can reduce nutritional quality. Opt for steaming, baking, or grilling instead.
7. Data Supports Moderation
A growing number of systematic reviews and dose-response meta-analyses have linked the consumption of ultra-processed food with adverse health outcomes like heart disease and diabetes.
However, sensitivity analyses show that moderate consumption of processed foods as part of a balanced, healthy diet can fit into a lifestyle without causing significant harm.
Image source: https://www.freepik.com/premium-photo/shallow-depth-field-image-nutrition-facts_34573525.htm#from_element=cross_selling__photo
Effects of Processed Food on Health
The health effects of processed foods depend largely on the type and amount consumed.
Studies show that statistically significant ultra-processed food consumption is linked to excess weight and adverse health outcomes, including chronic diseases.
High levels of saturated fat, added sugar, and food additives contribute to excessive consumption, excess calorie intake, and poor diet quality. On the other hand, consuming minimally processed items such as brown rice, fruits and produce, and lean meats supports better nutritional quality and may lower the risk of heart disease and breast cancer, according to systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
Processed Foods and Public Health
From a public health perspective, regulating ultraprocessed food consumption is becoming a priority worldwide.
The International Agency for Research on Cancer has classified some processed meats as carcinogenic, citing review and meta-analysis studies linking them to colorectal cancer. Public education campaigns encourage limiting excessive consumption of ultra-processed foods while promoting minimally processed and unprocessed foods.
Disclaimer: Everything in Moderation (including Processed Food)
Processed foods are a normal part of modern life, and they don’t have to be completely eliminated to maintain a good health status.
The key is to be aware of health risks and choose a healthy diet centered around minimally processed and whole foods while keeping ultra-processed food intake in check.
Processed foods aren’t necessarily bad; it’s the frequency, portion size, and overall balance in your diet that determine their health implications.

Camella Supports Your Healthy Lifestyle
Camella believes that a strong community begins with healthy residents.
Our master-planned communities feature spaces for walking, jogging, and safe food preparation at home. We encourage families to prioritize a healthy diet and better human health. Choose Camella and build a lifestyle that promotes wellness as much as it promotes comfort.

Celebrate Life’s Milestones in Camella!
Make unforgettable memories in a Camella home.
Our communities are designed to elevate your living experience.


